Recently The Motor Vehicle(Amendment) Bill passed by both houses including Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha after a long discussion. The new bill passed with a voice vote with 108 votes in favor and 13 against it. To make the road safer due to road accidents more than 1.5 lakh live lost yearly and also affect the nation. India loses more than $58 billion annually due to road accidents.
A new change made to Indian road to becoming safer. Now violaters will need to pay high traffic violation fine for violating the rules and stricter penalties in the case of offense by juveniles. Now traffic officer also has the power to suspend licenses of violators. A high tariff on violations makes the road safer.
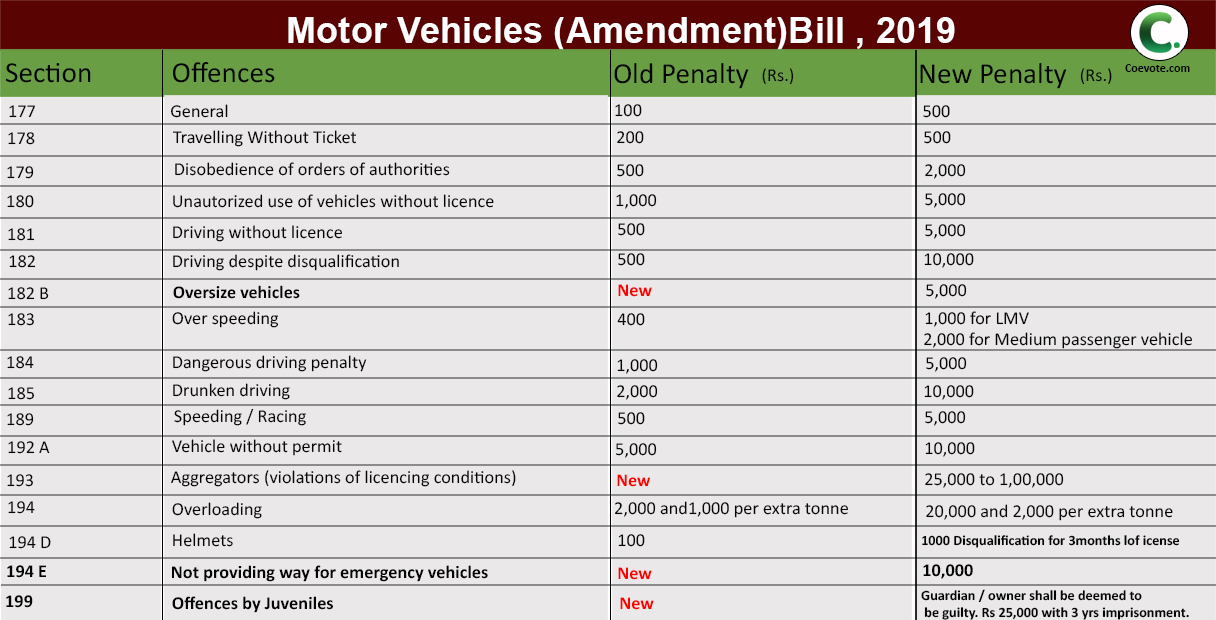
Key points of Motor Vehicle(Amendment) Bill, 2019 :
1. Offences and penalties: The Bill increases penalties for several offenses under the Act. For example, the maximum penalty for driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs has been increased from Rs 2,000 to Rs 10,000. If a vehicle manufacturer fails to comply with motor vehicle standards, the penalty will be a fine of up to Rs 100 crore, or imprisonment of up to one year, or both. If a contractor fails to comply with road design standards, the penalty will be a fine of up to one lakh rupees. The central government may increase fines mentioned under the Act every year by up to 10%.
2. Compensation for road accident victims: The central government will develop a scheme for cashless treatment of road accident victims during the golden hour. The Bill defines the golden hour as the time period of up to one hour following a traumatic injury, during which the likelihood of preventing death through prompt medical care is the highest. The central government may also make a scheme for providing interim relief to claimants seeking compensation under third party insurance. The Bill increases the minimum compensation for hit and run cases as follows: (i) in case of death, from Rs 25,000 to two lakh rupees, and (ii) in case of grievous injury, from Rs 12,500 to Rs 50,000.
3. Compulsory insurance: The Bill requires the central government to constitute a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund, to provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India. It will be utilized for: (i) treatment of persons injured in road accidents as per the golden hour scheme, (ii) compensation to representatives of a person who died in a hit and run accident, (iii) compensation to a person grievously hurt in a hit and run accident, and (iv) compensation to any other persons as prescribed by the central government. This Fund will be credited through: (i) payment of a nature notified by the central government, (ii) a grant or loan made by the central government, (iii) balance of the Solatium Fund (existing fund under the Act to provide compensation for hit and run accidents), or (iv) any other source as prescribed the central government.
4. Good samaritans: The Bill defines a good samaritan as a person who renders emergency medical or non-medical assistance to a victim at the scene of an accident. The assistance must have been (i) in good faith, (ii) voluntary, and (iii) without the expectation of any reward. Such a person will not be liable for any civil or criminal action for any injury to or death of an accident victim caused due to their negligence in providing assistance to the victim.
5.Taxi aggregators: The Bill defines aggregators as digital intermediaries or market places which can be used by passengers to connect with a driver for transportation purposes (taxi services). These aggregators will be issued licenses by the state Further, they must comply with the Information Technology Act, 2000.
You can Know More about Changes on PRS India
Importance of the Bill
Union Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Lok Sabha that more than 1.50 lakh people die and 5 lakh people injured annually in road accidents. The amendment Bill proposes to exclude a clause of the Motor Vehicle Act to decide how to maintain their registers for driving licenses, to centralize vehicle registration data and achieve standardization.
Reasons of road accidents in India
The Standing Committee on Transport had observed that the majority of accidents being caused due to driver’s fault may be erroneous. Other reasons for road accidents include fault of drivers of other vehicles, defect in the condition of a motor vehicle, fault of pedestrian, weather conditions, faulty road engineering, etc.